No time like a present: heart disease, metabolic syndrome and weight
Want to give yourself the gift of a lifetime? Aim for a healthy weight before you hit menopause.
We’ve discussed it time and again on Flashfree; weight gain and menopause go hand in hand like a horse and carriage. And with that weight gains comes an increased risk for developing heart disease, diabetes and the dreaded metabolic syndrome. However, researchers from the University of Ottawa are reporting that entering full menopause with a healthy body mass index (BMI) actually confers protection.
In the study (which appeared online a few weeks ago in the journal Menopause), researchers evaluated and observed 102 premenopausal women for body composition and changes in their cardiovascular health profiles. The women, all of whom were between 47 and 55 years of age, did not smoke, had a BMI between 20 and 29 and had had a stable weight for at least 6 months before the study started, were followed for five years. Each year, the researchers gauged if they had entered menopause, measured body composition (i.e. total fat mass, trunk fat mass and total fat free mass), waist size, the degree of abdominal fat and took blood to examine glucose, insulin and blood fat levels.
The study’s lead researcher, Dr. Denis Prud-homme explains that by simply observing the women and not imposing any structured interventions (e.g. diet or exercise) they were able to assess changes within a more naturalistic environment. At the study’s end, they discovered that despite significant increases in fat mass, visceral abdominal fat, blood glucose and cholesterol levels, most of which were the natural result of hormone fluctuations and aging, the women did not appear to have any declines in their heart or metabolic profiles that would indicate an increased risk for disease. Dr. Prud-homme says that a possible explanation might be that “even if the area of visceral fat is increased, it is still under the critical threshold associated with cardio-metabolic deterioration.” In other words, by maintaing a healthy lifestyle and BMI premenopausally, these women were able to change their risk equations once they fully entered menopause.
The bottom line is that the present you give yourself now will last long into your later years. Exercise. Eat right. And pay attention to your health.
No time like the present. For a present. Give yourself one.
Read MoreFish oil. One of these is not like the others…
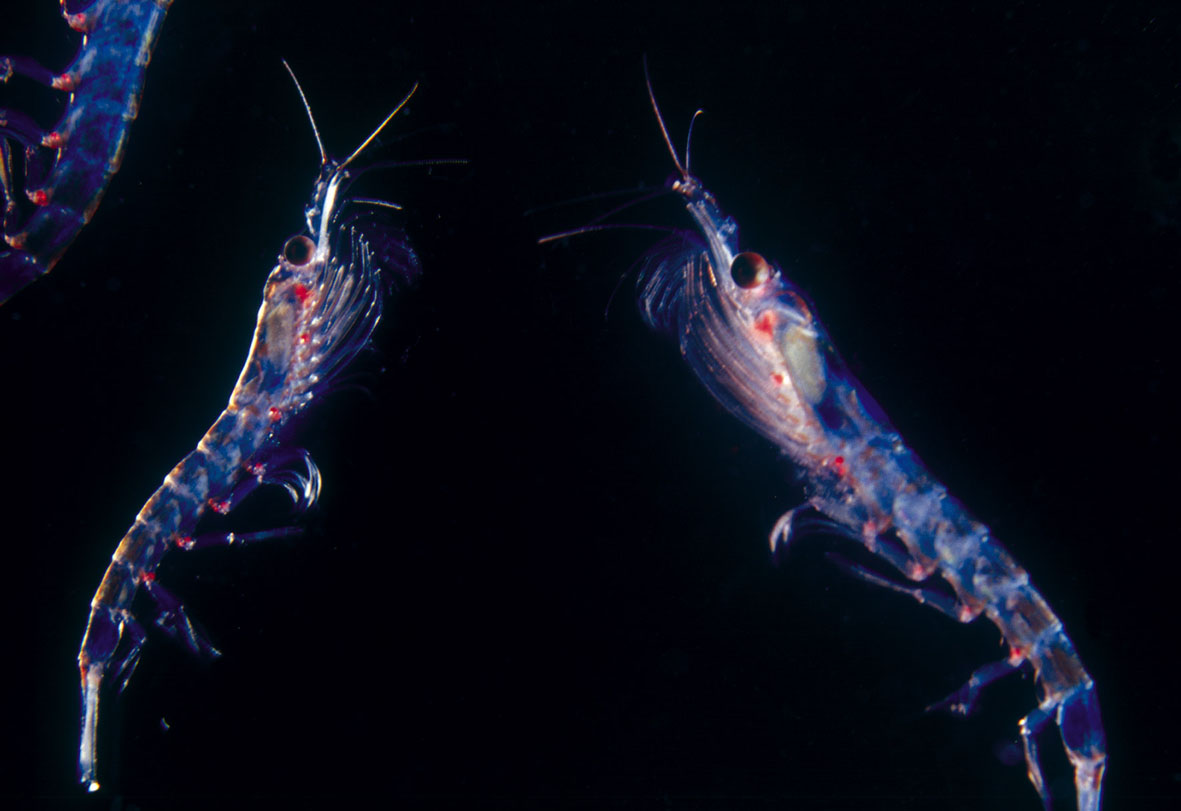
[Photo credit: Australian Government Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. Australian Antarctic Division. ™2004.
Fish oils. Love em or hate em, they’re here to stay. And researchers will continue to research the hell out of these substances — namely omega 3 fatty acids — until they solve the question of ‘do they or don’t they?’ Meanwhile, true confession: as much as I’ve attempted to take fish oil supplements or flaxseed oil per health practitioner recommendations, I’ve always failed horribly. It’s the burp factor. They make me burp and I taste fish all day long. Can’t stand it. Or Stomach it. Or something.
And then I was contacted by the folks over at Everest Nutrition Corporation about its krill oil supplement. And I’ve been reborn.
Let me give you a brief overview of omega-3s and then the lowdown on krill. And why I’ve been converted.
Early last year I wrote a post on research that examined if some of the most commonly used ingredients in supplements may or may boost certain components of mental energy. Here’s an excerpt (although if you’d like to read the post in its entirety, you can find it here):
Omega-3 fatty acids I love fish oils. Researchers continue to study them because their utility is so broad, although the source of omega-3, dosage and ratio of EPA and DHA appear to be important factors in terms of mood (i.e. depression in particular) and mental energy. Overuse of fish oils can also impair the ability of blood to clot and depress overall immune functioning. Still, out of the dietary components that researchers studied, omega-3′s were by far the one most backed by clear data. Most recently, they’ve also been shown to help prevent stroke. In so far as mental energy goes, the researchers note that evidence suggests that fish oils may help delay or reduce cognitive decline in the elderly or improve verbal fluency. Less clear is whether this benefit is stronger if the they are taken earlier in life before cognitive decline. And of course, there is litte agreement on whether or not fish oils supplements convey the same benefits as obtaining the through dietary sources. And, if you choose to obtain your omega-3s through supplementation or pure oil, there is the issue of overfishing of the world’s oceans and how fish oil preparations may contribute to the problem.
So what about fish oil supplements derived from krill?
Krill are small, shrimp-like crustracean that feed on microscopic organisms in the ocean called phytoplankton. Compared to other sources of omega-3s, krill is in less danger of being overfished, one reason why it is so attractive. However, the omega 3s in krill oil attach themselves to fats the form cell membranes (phospholipids), rather than triglycerides, which theoretically makes krill derived omega-3 fatty acids more effective reducing fats in the heart and liver. Another benefit of krill oil is that it contains an antixidant called astaxanthin, which helps protect the body from damage by UV rays, and can help reduce LDL-cholesterol levels while raising HDL-cholesterol levels. Moreover, astaxanthin crosses the blood brain barrier, meaning that it might be of use in protecting eyes, the brain and the central nervous system from circulating free radicals.
However, buyer beware! Not all krill oils are created equal and you want to be certain that what you’re buying meets the highest standards in terms of:
- Meeting content claims about levels of ecosapentaenoic acid (EPA), doxosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and phospholipids
- Meeting claims about how much astaxanthin is delivered per capsule
- If the formulation meets standards for purity, safety and cleanliness per International Krill Oil Standards (IKOS)
- If the product is stable
- If the product meets the standards for contents of heavy metals and mercury
You also need to know that krill oil should not be taken by people with shellfish allergies. Additionally, some people report having gastrointestinal issues, e.g. diarrhea, loose stools when taking krill oil; this is due to the fatty acid that is present in the oil, and may be alleviated by taking a lower dose. Like other forms of fish oil, krill oil may also thin the blood and impair its ability to clot, and in some cases, may interact with thyroid medication. Pregnant women should speak to their doctors before trying krill oil.
Like many other forms of omega-3 fatty acids, krill oil can be expensive. A 30-day supply of Everest Nutrition’s Krill Oil costs roughly $30 a month, which comes out to $1 a day or $.50 a capsule.
So, what do I think? I’m a believer. I have had physicians and other healthcare practitioners recommend that I take fish oil for as long as I can remember. And I haven’t because of the burp factor. I’m grateful to have discovered krill oil. And I highly recommend Everest Nutrition’s formulation, primarily because the manufacturer adheres to the highest of standards.
[Disclaimer: I was not paid to write this review of Everest Nutrition Krill Oil. However, company representatives did provide me with product to try.]
Read More
Wednesday Bubble: diabetes and the ‘pause
When I saw a post on my Facebook stream linking hormonal imbalance to diabetes, I become intrigued, ever more so when I ran across the following headline in my daily newsfeed:
“Does menopause matter when it comes to diabetes?”
So, does it or doesn’t it?
According to the first piece that resides on the website of the hormone franchise, BodyLogic MD, imbalances of hormones other than insulin can promote insulin imbalances or resistance that is especially evident during menopause. Their hypothesis? Hormone replacement will correct these imbalances and prevent millions of women from developing diabetes.
In fact, there is evidence that as endogenous androgen levels rise and estrogen levels fall, there is a predisposition to glucose intolerance (i.e. a struggle to convert blood sugar or glucose into energy) and by default, diabetes. Moreover, estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce fasting blood glucose levels in menopausal women (fasting blood glucose or sugar measures glucose levels in the bloodstream and is a test for pre- and full blown diabetes). However, it is unknown if menopause itself is associated with high glucose levels or plays a role in influencing factors such as insulin secretion and insulin resistance that mediate glucose tolerance. Nevertheless, it is possible that menopause status may tip the scales in women who are already at high risk for diabetes or even influence activities undertaken to prevent the condition.
In a soon to be published study (August issue, Menopause journal), researchers compared perimenopausal women to women who had entered menopause naturally and those who had had their ovaries removed. All participants were between the ages of 45 and 58, and part of a larger Diabetes Prevention Program trial, meaning that they already had been diagnosed with having impaired glucose tolerance and fasting glucose levels and were at risk for diabetes. Of the 1,237 women studied, they had either been assigned twice daily diabetes medication (Metformin), twice-daily placebo tablet or an intensive lifestyle intervention to achieve and maintain a weight reduction of at least 7% (through a low-calorie, low-fat diet, and at least 150 minutes moderate physical activity weekly).
Read MoreWednesday Bubble: I’ve got the blues and it’s all good!

I’ve got the blues this week; blueberries that is. And the news is all good!
Researchers at the University of Michigan at Ann Arbor are reporting that eating a diet rich in blue berries might reduce heart disease, protect against diabetes, and get rid of belly fat! Is this too good to be true? And what does this have to do with menopause anyway?
I’ve written previously on increased risk of heart disease and increased likelihood of gaining weight around the abdominal region as we age. So, if blueberries can potentially help to stave off both, that’s great news, right?
The research team studied the effect of a blueberry-enriched powder added to either a low-fat or high-fat diet in laboratory rats and compared them to rats receiving no blueberry powder. The rats were of a particular breed that are prone to weight gain and being severely overweight.
After 90 days, rats receiving the blueberry powder (which comprised 2% of their total diet) had less abdominal fat, and lower triglycerides and cholesterol levels. They also showed improvements in fasting blood glucose and insulin sensitivity, which measures the risk for diabetes and heart disease (namely metabolic syndrome), respectively.
What’s more, the benefits were even greater among rats fed the powder along with a low-fat diet: they had lower body weight, lower total fat mass, and reduced liver mass (which has been linked to obesity and insulin resistance) than rats in the other study groups. The researchers also reported positive changes in measures such as fat muscle tissue (which relates to fat-burning and storage) in rats fed the blueberry powder and a high-fat diet.
The beneficial effects of blueberries are believed to be possibly related to inherently high levels of an antioxidant known as anthocyanins, which is responsible for blueberries’ colour.
Clearly, further research, is needed, particularly in humans. In the interim, eat some blueberries: they’re high in flavor, a great source of fiber and vitamins C and K, and low in fat. And may help combat some of the less attractive pitfalls of mid-life.
Read More